CPU Burst #
As its core, a CPU burst is a period during which a program(task) demands and actively utilizes the CPU for computation.
CPU bursts have two typical characteristics:
- duration
- variability
Long CPU bursts are mostly common in CPU-intensive computing scenarios. Some applications that showcase.
Identifying the length and variability of CPU bursts is an important step when doing performance optimization in systems.
Duration #
CPU bursts can vary significantly in duration. Some may be short and intensive, while others may be long and less resource-demanding. Understanding the duration of CPU bursts helps in resource allocation and task scheduling.
Variability #
The variability of CPU bursts is a critical factor in system performance. Burst patterns can be irregular, leading to unpredictable system behaviour. Managing this variability is essential for maintaining system stability.
I/O Burst #
I/O bursts involve Input/Output operations. During an I/O burst, a program(task) waits for data to be read from or written to external storage devices, such as disks or network resources. I/O bursts are common in scenarios where data needs to be fetched from or delivered to external sources.
I/O bursts also have two typical characteristics:
- the time a process waits for data to be retrieved or stored.
- various types of operations, including disk I/O, network I/O, and more.
As we would expect, there exist workloads that are more I/O intensive and, therefore, require more I/O bursts. Those may include things like database operations, where data is retrieved or stored on disk, web servers handling numerous client requests or video streaming, where data is constantly read from storage(or network).
To optimize I/O performance, it is crucial to measure and analyze I/O bursts. We can use tools like iostat and sar.
Relationship between CPU and I/O Bursts #
In many scenarios, CPU and I/O bursts are interconnected. For example, a web server may experience CPU bursts while processing requests and I/O bursts when reading or writing data to storage. Balancing the utilization of CPU and I/O resources is essential for OS performance.
We can see how one program(task) changes between CPU and I/O utilization while running:
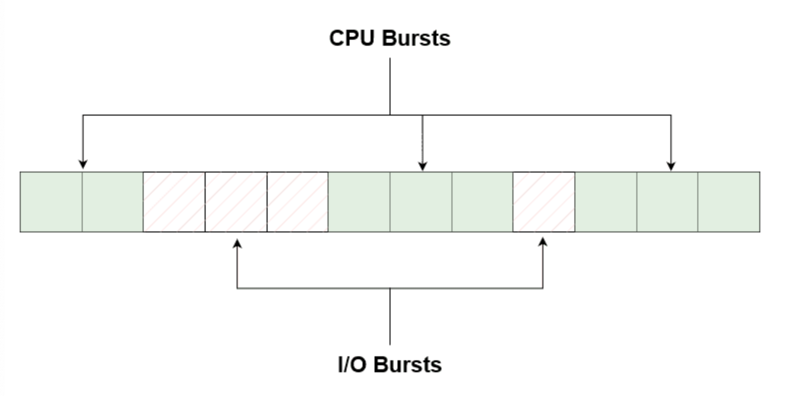
Here are two scenarios:
- Database Management - DB systems often face a delicate balance between CPU intensive query processing and I/O bound data retrieval. Optimizations, such as indexing and caching, are used to minimize the impact of bursts on database performance.
- Web Server - Web servers encounter bursts of incoming requests that require CPU processing. Additionally, serving static assets like images or videos involves I/O bursts. Efficient request handling and caching strategies are crucial in maintaining responsive web services.
Strategies for Handling Bursts #
For CPU bursts #
A big part of resource allocation is task scheduling. OS use scheduling algorithms to manage CPU bursts. Prioritizing tasks based on their urgency and resource requirements ensures fair resource allocation.
Parallel processing is equally important and helps greatly improve performance on CPU bursts.
For I/O bursts #
Caching is probably the most effecitve strategy with regard to I/O bursts. This approach minimizes the need to retrieve data from slower storage devices.
Asynchronous I/O is allowing processes to continue execution while waiting for I/O operations to complete asynchronously. With this step, systems can maximize CPU utilization and responsiveness.