6-Caching Strategies to Remember while designing Cache System
Key Metrics #
- 캐시 히트율 (cache hit ratio)
- 응답 시간 (latency)
- 처리량 (throughput)
- 캐시 사이즈 (cache size)
- 캐시 미스율 (cache miss ratio)
Read Intensive Application Caching #
- Cache-aside
- Cache-through
- Refresh-ahead
Cache-aside #
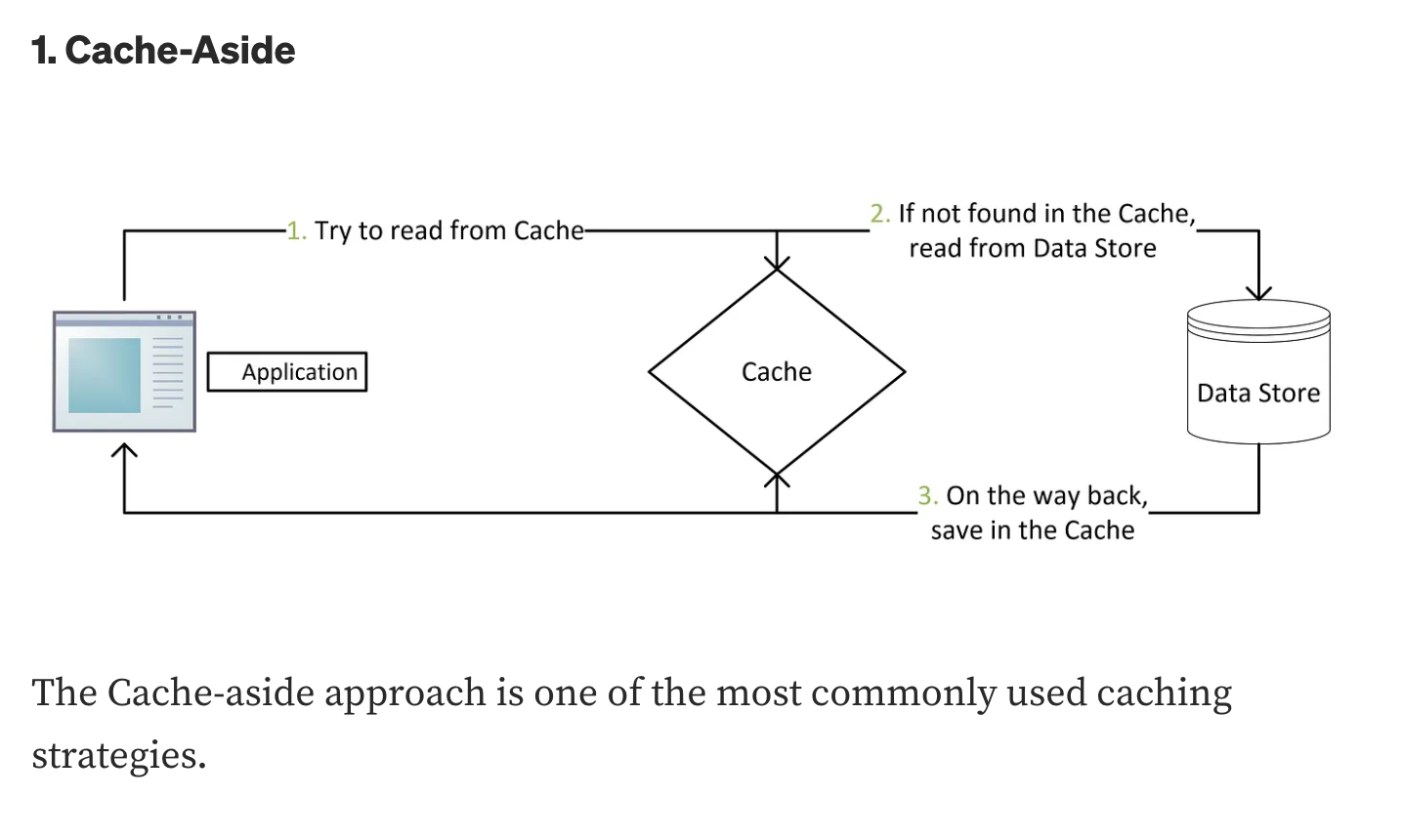
- 캐시가 미스됐을 때, 3번의 trip 이 발생해 급격한 딜레이가 생길 수 있다.
- 데이터베이스에 업데이트하고 캐시에는 업데이트를 누락하여 캐시의 데이터가 낡은 상태로 유지될 수 있다.
" Data might become stale if someone updates the database without writing to the cache. (Hence, Cache-aside is usually used alongside other strategies). “
Read-through #
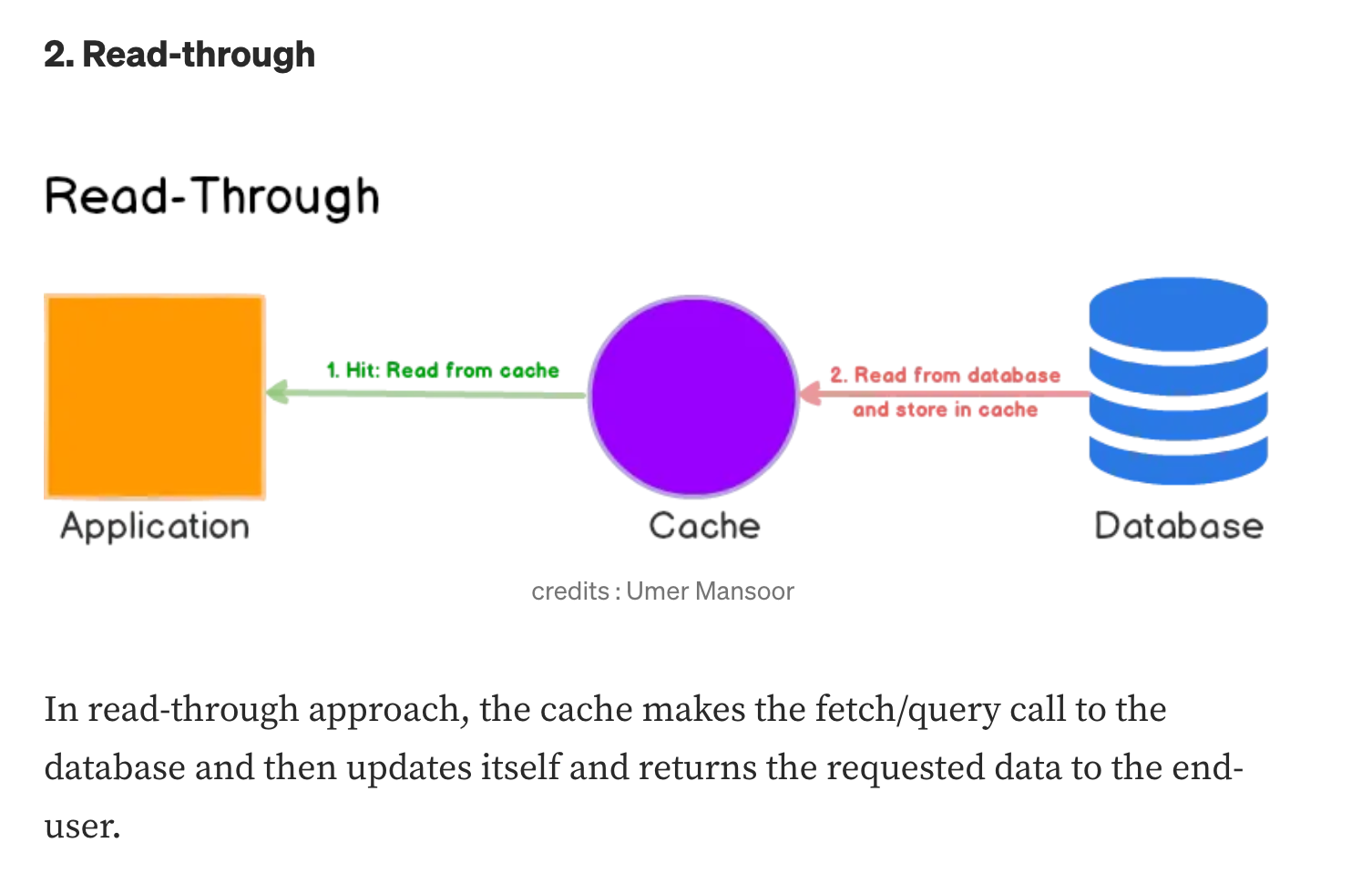
Cache-aside 와 비슷하지만, 애플리케이션이 캐시에만 질의하고, (캐시 미스 상태인 경우) 캐시가 DB에 질의하는 차이가 있다.
- Read-through 는 (애플리케이션 -> 캐시 -> DB)흐름/로직이 단순해진다.
- Better read scalability. Cache-aside 에서 키가 만료된 경우, 동시 요청이 발생해 DB에 여러번 질의할 수 있다. 그러나 Read-through의 경우, (동시 요청이 발생해도)DB에는 오직 1번의 쿼리만 질의되는 것이 보장된다.
(아마도 흐름은…)
- 캐시에 동시 여러개의 요청이 왔을 때 그 중 하나의 처리에서 업데이트(DB로부터 데이터 질의 & 업데이트)
- 이때 나머지 요청은 블락(큐잉) 상태
Refersh-ahead #
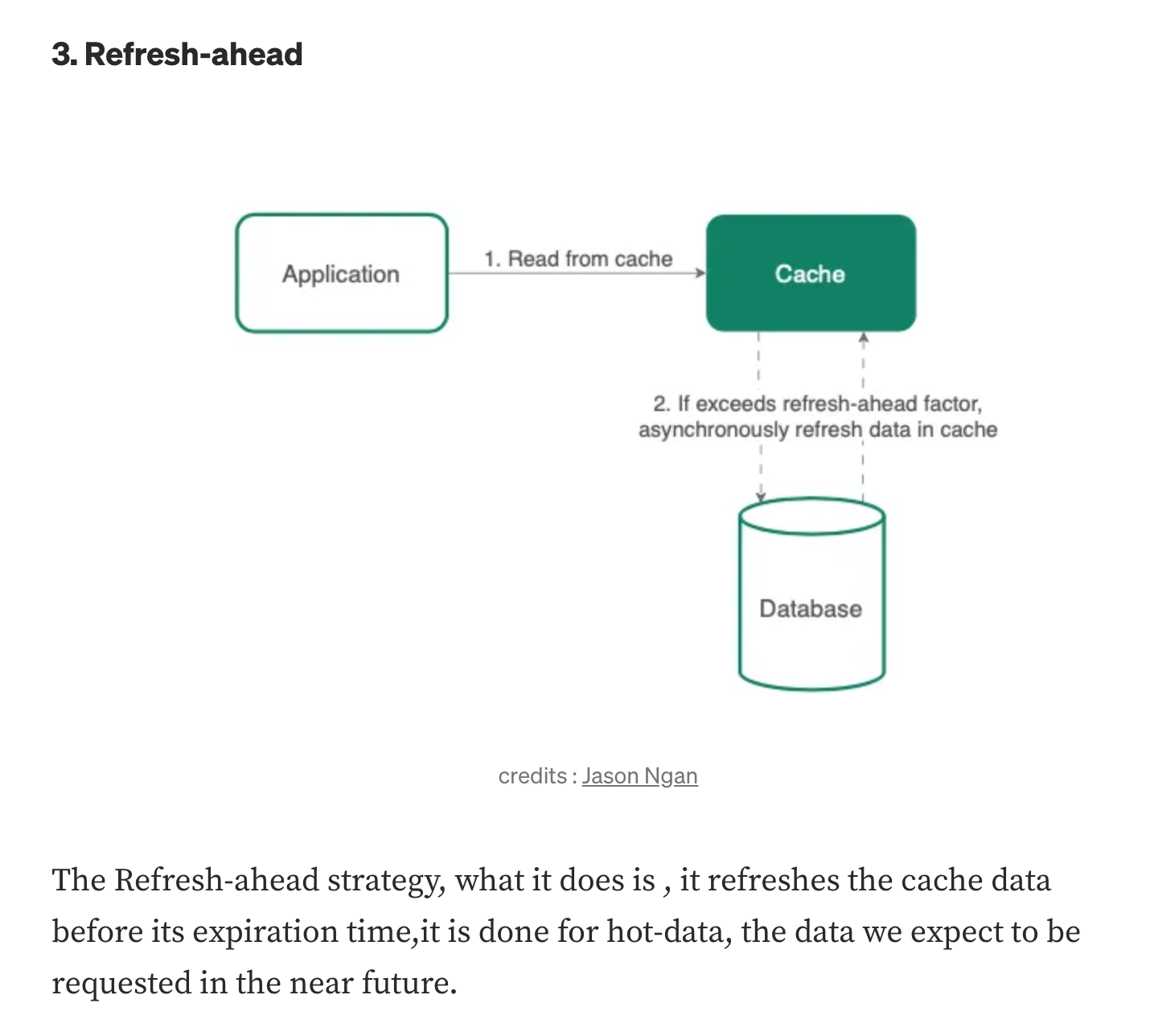
” So what refresh ahead caching does is it essentially refreshes the cache at a configured interval just before the next possible cache access although it might take some time due to network latency to refresh the data & meanwhile few thousand read operation already might have happened in a very highly read heavy system in just a duration of few milliseconds. “
Write Intensive Application Caching #
- Write-through
- Write-back (Write-behind)
- Write-around
Write-through #
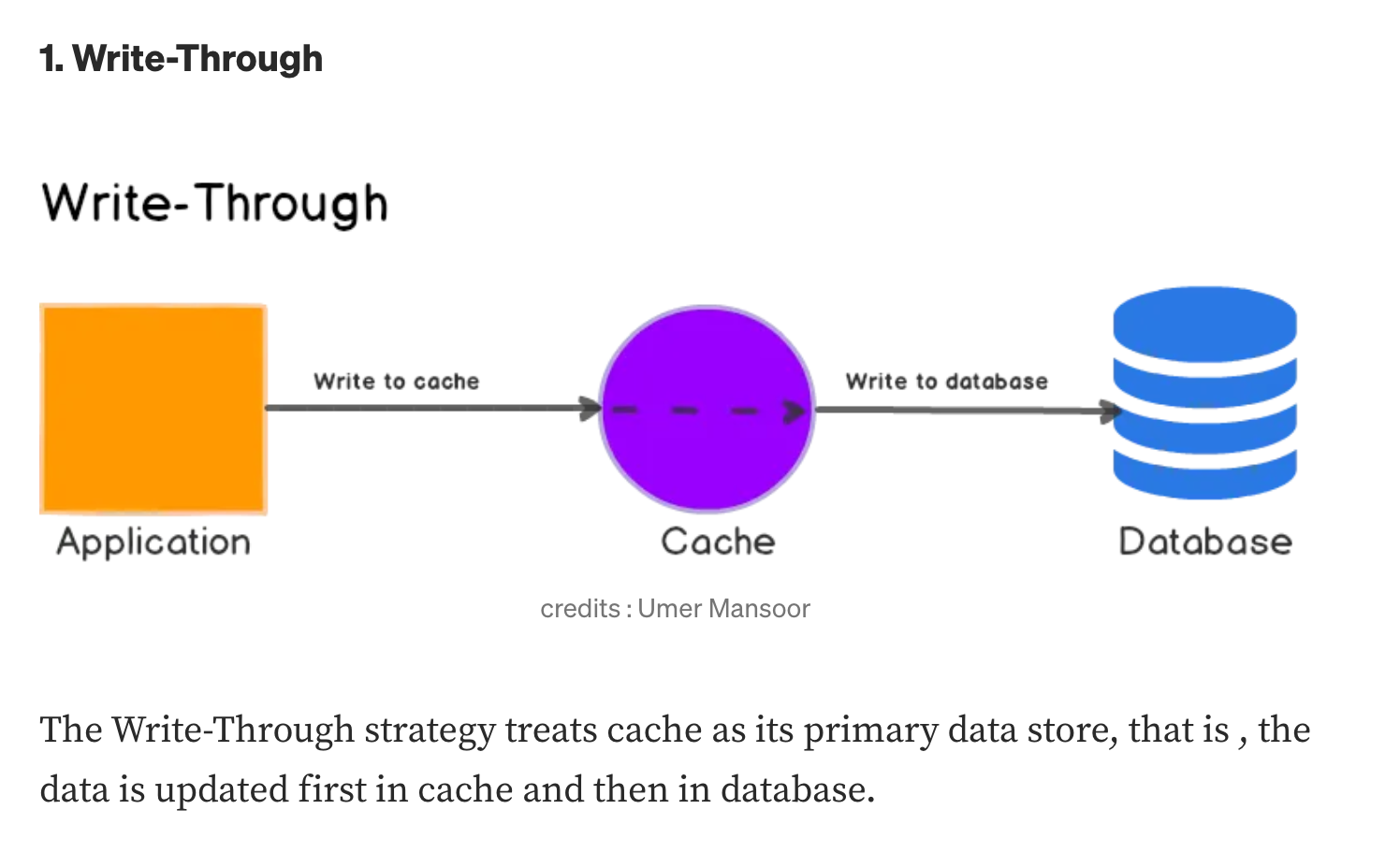
" The Write-Through strategy treats cache as its primary data store, that is , the data is updated first in cache and then in database. "
Read-through 와 비슷하다. Write-through 는 캐시가 primary data store 로 취급되는 것과 마찬가지다.
- Read-through 전략과 같이 사용될 때, 효율적인? 적절한 구조가 되겠다.
- 캐시의 데이터는 항상 최신 상태로 유지될 것이고, DB와 캐시의 데이터가 (거의)일치하겠다.
Write-back #
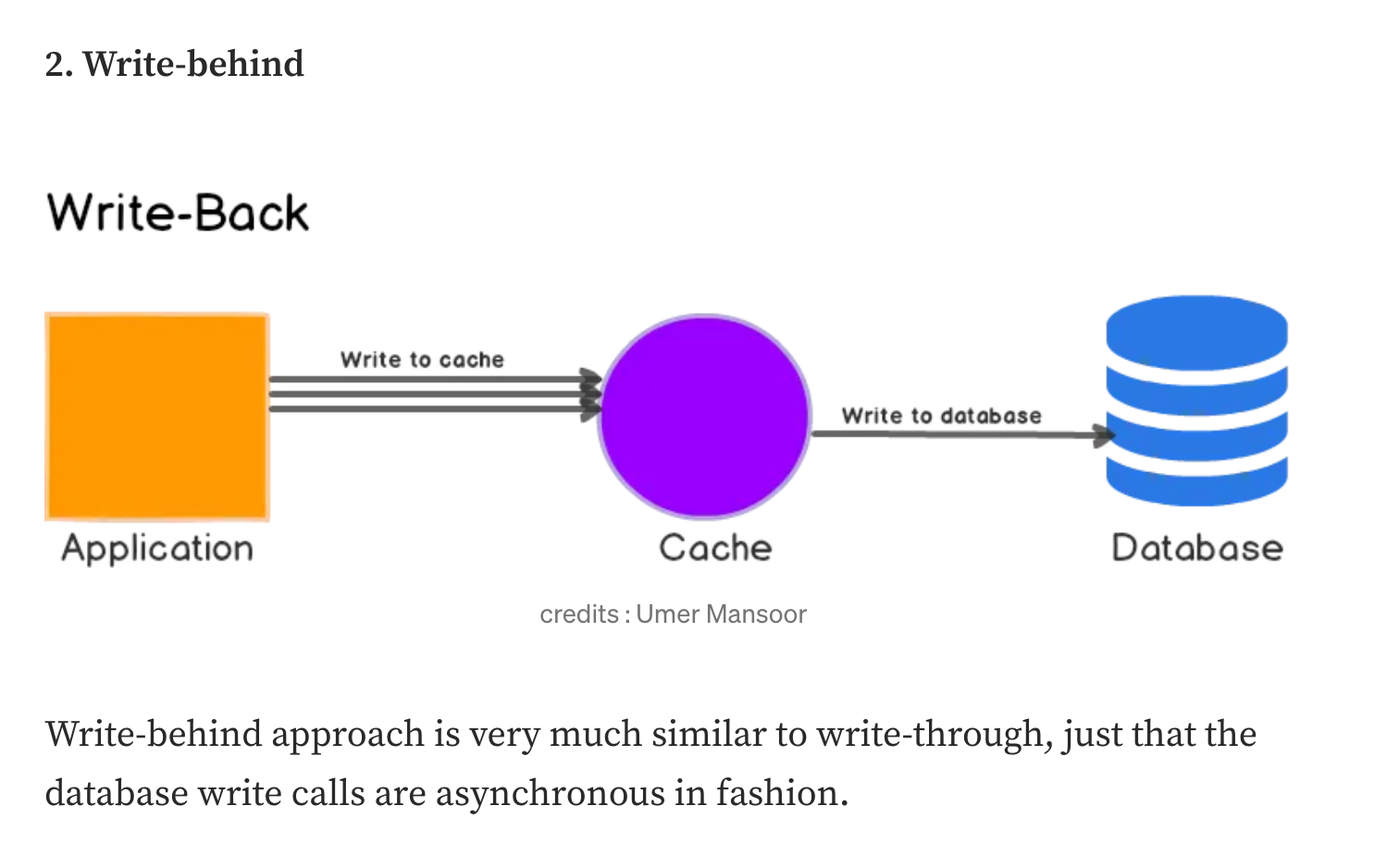
write-through 와 유사하지만, DB 동기화를 비동기로 처리하는 점이 다르다.
캐시에 먼저 쓰기 때문에(= 최신화된 데이터가 유지되기 때문에)읽기 작업, (비동기로 DB에 쓰기 때문에) 쓰기 작업 모두에 적합하다.
- 쓰기 성능이 향상된다. (많은 양의 write 가 발생해도 대응할 수 있다.)
- 네트워크 비용을 줄일 수 있다.
- 비동기로 처리할 때 배치성으로 처리하면 네트워크 콜 수(비용)를 줄일 수 있다.
- 캐시에 먼저 쓰기 때문에 자주 요청되지 않은 데이터도 캐시에 기록된다. (즉, 불필요한 데이터도 함께 쌓인다.)
- 이런 데이터는 TTL 설정으로 최소화시킬 수 있다.
위 특징 중 읽기 요청에 대응할 수 있다는 점과, 3번은 Write-through 에도 동일할 것이다. (
캐시에 먼저 쓰는 행위가 같기 때문에)
Write-around #
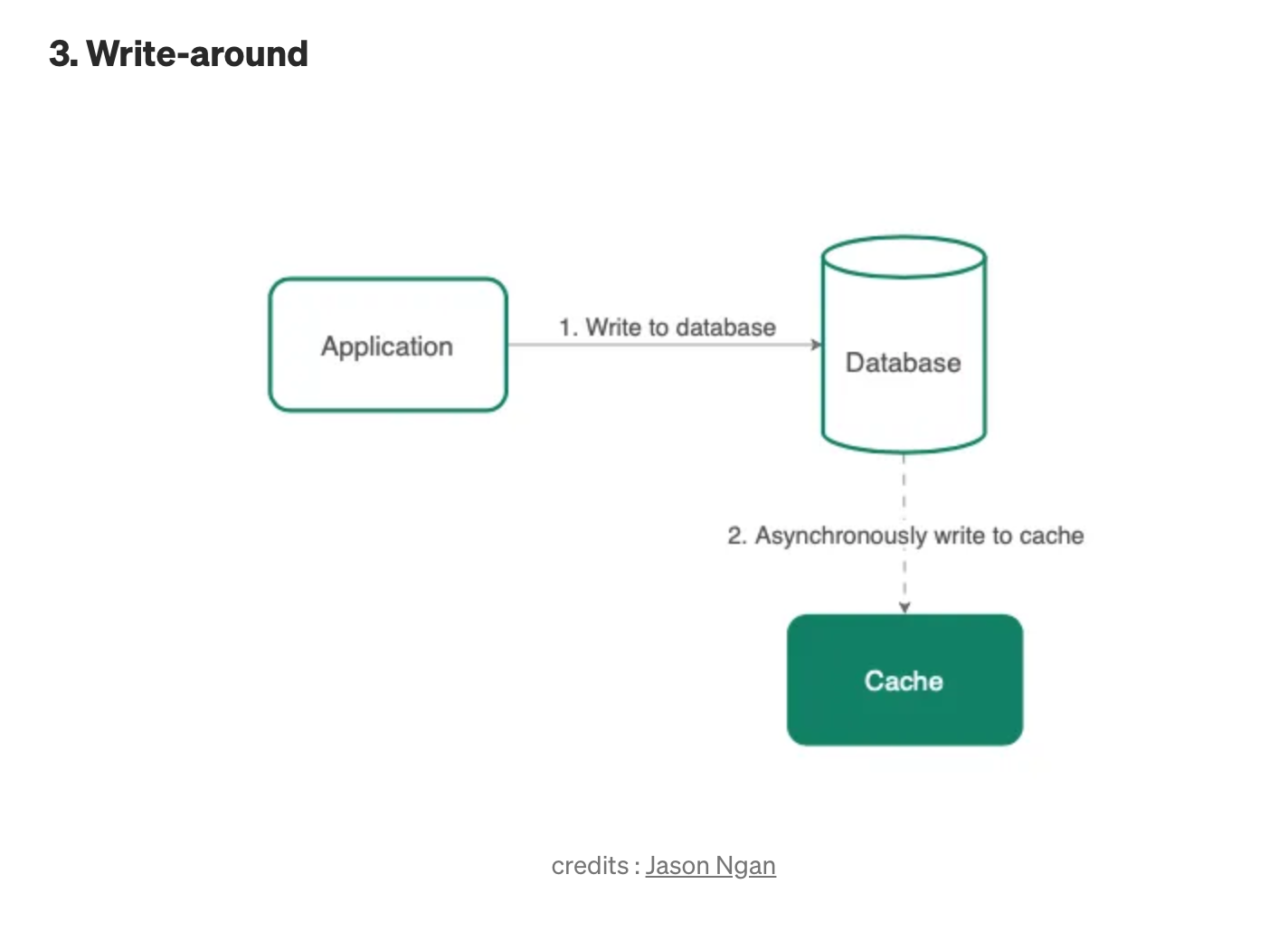
읽기 작업이 빈번하지 않을 때 (=데이터가 한 번 쓰이고 안읽히거나 조금 읽힐 때) 사용될 수 있다. (로그성 데이터 등)
Cache Invalidation Methods #
Cache invalidation : the process of removing stale or outdated data from a cache
몇 가지 전략은 다음과 같다.
- Time-based invalidation (TTL)
- Event-based invalidation
- This is a more targeted approach to invalidation that ensures that data is invalidated only when necessary.
- Version-based invalidation
- 데이터에 버저닝을 하고, 업데이트 시 마다 버전을 올린다. 가장 최신 버전의 데이터만 사용된다.
- 데이터가 빈번하게 변경될 때 사용될 수 있지만 :thinking:, 버전을 관리해야하니 추가 오버헤드가 발생한다.
- LRU invalidation
- Manual invalidation