Spring MVC : Error #
핵심 클래스 / 인터페이스 #
| class (interface) | 설명 |
|---|---|
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration | (MVC) Error Controller 관련 Auto-configuration 클래스 |
ErrorController | Error Controller 인터페이스 하위 : AbstractErrorController, BasicErrorController |
BasicErrorController | Error Controller 구현 클래스 Spring Web(MVC)에서 Default 로 사용되는 구현체 (with DefaultErrorViewResolver) |
ErrorProperties | (위에서 사용되는) Error property 클래스 Path, WhiteLabel, … |
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
#
// Load before the main WebMvcAutoConfiguration so that the error View is available
@AutoConfiguration(before = WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
...
static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
...
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(
this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage); // ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry => TomcatServletWebServerFactory (AbstractConfigurableWebServerFactory)
}
...
}
ErrorPageCustomizer.registerErrorPages(...)
/error경로에 대한ErrorPage가 생성된다.- 생성된
ErrorPage는 errorPageRegistry 에 등록된다.
TomcatServletWebServerFactory.configureContext(...)
TomcatEmbeddedContext의ErrorPageSupport에org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage가 등록된다.- 이후에 에러가 발생했을 때,
ErrorReportValve>StandardHostValve.invoke(...)>StandardHostValve.status(...)>TomcatEmbeddedContext.findErrorPage(...)순서로ErrorPage를 찾게 된다. (찾은 ErrorPage로 request를 forwarding)(ApplicationDispatcher, RequestDispatcher) rd.forward(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
- (아래 코드 참고)
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory
extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory
implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware {
...
protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers);
if (context instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext) {
TomcatEmbeddedContext embeddedContext = (TomcatEmbeddedContext) context;
embeddedContext.setStarter(starter);
embeddedContext.setFailCtxIfServletStartFails(true);
}
context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : this.contextLifecycleListeners) {
context.addLifecycleListener(lifecycleListener);
}
for (Valve valve : this.contextValves) {
context.getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
for (ErrorPage errorPage : getErrorPages()) {
org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage tomcatErrorPage = new org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage();
tomcatErrorPage.setLocation(errorPage.getPath());
tomcatErrorPage.setErrorCode(errorPage.getStatusCode());
tomcatErrorPage.setExceptionType(errorPage.getExceptionName());
context.addErrorPage(tomcatErrorPage);
}
...
/**
* Valve that implements the default basic behavior for the
* <code>StandardHost</code> container implementation.
* <p>
* <b>USAGE CONSTRAINT</b>: This implementation is likely to be useful only
* when processing HTTP requests.
*
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
final class StandardHostValve extends ValveBase {
...
/**
* Select the appropriate child Context to process this request,
* based on the specified request URI. If no matching Context can
* be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
...
try {
...
// Look for (and render if found) an application level error page
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
// If an error has occurred that prevents further I/O, don't waste time
// producing an error report that will never be read
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
}
...
}
...
}
private void status(Request request, Response response) {
int statusCode = response.getStatus();
// Handle a custom error page for this status code
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
return;
}
/* Only look for error pages when isError() is set.
* isError() is set when response.sendError() is invoked. This
* allows custom error pages without relying on default from
* web.xml.
*/
if (!response.isError()) {
return;
}
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(statusCode);
if (errorPage == null) {
// Look for a default error page
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(0); // <-- 여기!
}
...
}
...
}
ErrorController
#
/**
* Marker interface used to identify a {@link Controller @Controller} that should be used to render errors.
*/
public interface ErrorController {
}
BasicErrorController
#
/**
* Basic global error @Controller, rendering ErrorAttributes.
* More specific errors can be handled either using Spring MVC abstractions (e.g. @ExceptionHandler) or by adding servlet server error pages.
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
...
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
...
Spring 예외 처리 흐름 #
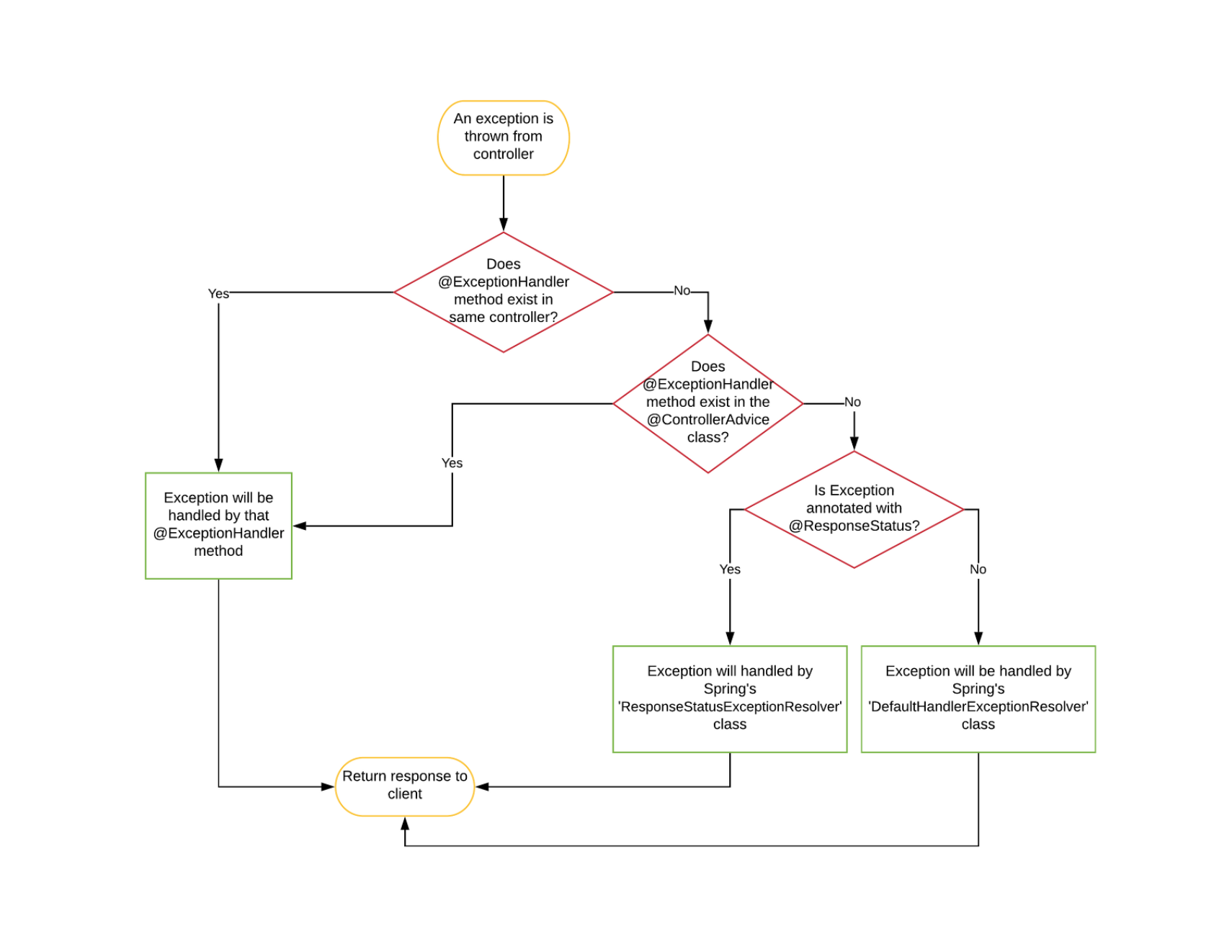
출처 : [Spring] Spring의 다양한 예외 처리 방법(ExceptionHandler, ControllerAdvice 등) 완벽하게 이해하기 - (1/2)
WebMvcConfigurationSupport 클래스를 참고하면, 아래 순서로 register 되는 것을 알 수 있다. (addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers())
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
/**
* Registers a HandlerExceptionResolverComposite with this chain of exception resolvers:
*
* - ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver for handling exceptions through org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler methods.
* - ResponseStatusExceptionResolver for exceptions annotated with org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus.
* - DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver for resolving known Spring exception types
*/
public class WebMvcConfigurationSupport implements ApplicationContextAware, ServletContextAware {
...
protected final void addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> exceptionResolvers,
ContentNegotiationManager mvcContentNegotiationManager) {
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver exceptionHandlerResolver = createExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver();
exceptionHandlerResolver.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager);
exceptionHandlerResolver.setMessageConverters(getMessageConverters());
exceptionHandlerResolver.setCustomArgumentResolvers(getArgumentResolvers());
exceptionHandlerResolver.setCustomReturnValueHandlers(getReturnValueHandlers());
if (jackson2Present) {
exceptionHandlerResolver.setResponseBodyAdvice(
Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewResponseBodyAdvice()));
}
if (this.applicationContext != null) {
exceptionHandlerResolver.setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
exceptionHandlerResolver.afterPropertiesSet();
exceptionResolvers.add(exceptionHandlerResolver);
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver responseStatusResolver = new ResponseStatusExceptionResolver();
responseStatusResolver.setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
exceptionResolvers.add(responseStatusResolver);
exceptionResolvers.add(new DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver());
}
이 클래스(주석 내용)는 중요하다. 별도로 살펴보자.