Intro #
W3C 는 2019년 비밀번호 없는 로그인을 위한 공식 웹 표준 명세 ‘WebAuth’ 을 발표했다.
WebAuthn 은 비밀번호 대신 public key cryptography 를 사용해 인증할 수 있는 W3C, FIDO 명세다. 혹은 생체 인식, 하드웨어 기반 인증과 같은 다양한 인증 방식을 사용해 서비스(웹사이트)에 로그인할 수 있는 방법을 제안하는 W3C API 명세다.
WebAuthn 은 public key cryptography 를 사용하기에 피싱 공격을 예방할 수 있다. 또, 업계 표준 암호화 알고리즘, 프로토콜을 사용해 보안을 보장한다.
Glossary #
- Relying Party(RP) : 서비스 제공자(웹사이트)
- WebAuthn Client Device : 사용자가 사용하는 디바이스 (e.g., smartphone, computer)
- Authenticator : 사용자를 인증하는 장치
- User : 사용자
Authenticator #
두 종류의 authenticator 가 있다.
- platform authenticator
- roaming authenticator
Platform Authenticator #
사용자의 디바이스 혹은 플랫폼에 내장되어 있다. (e.g., fingerprint sensor, face recognition)
Roaming Authenticator #
플랫폼이나 디바이스에 종속되지 않는 authenticator 이다. ‘cross-platform’, ’external authenticators’라고 부르기도 한다. (e.g., hardware security keys like the YubiKey).
How Works #
Registration Flow, Authentication Flow 두 가지를 살펴볼 수 있다.
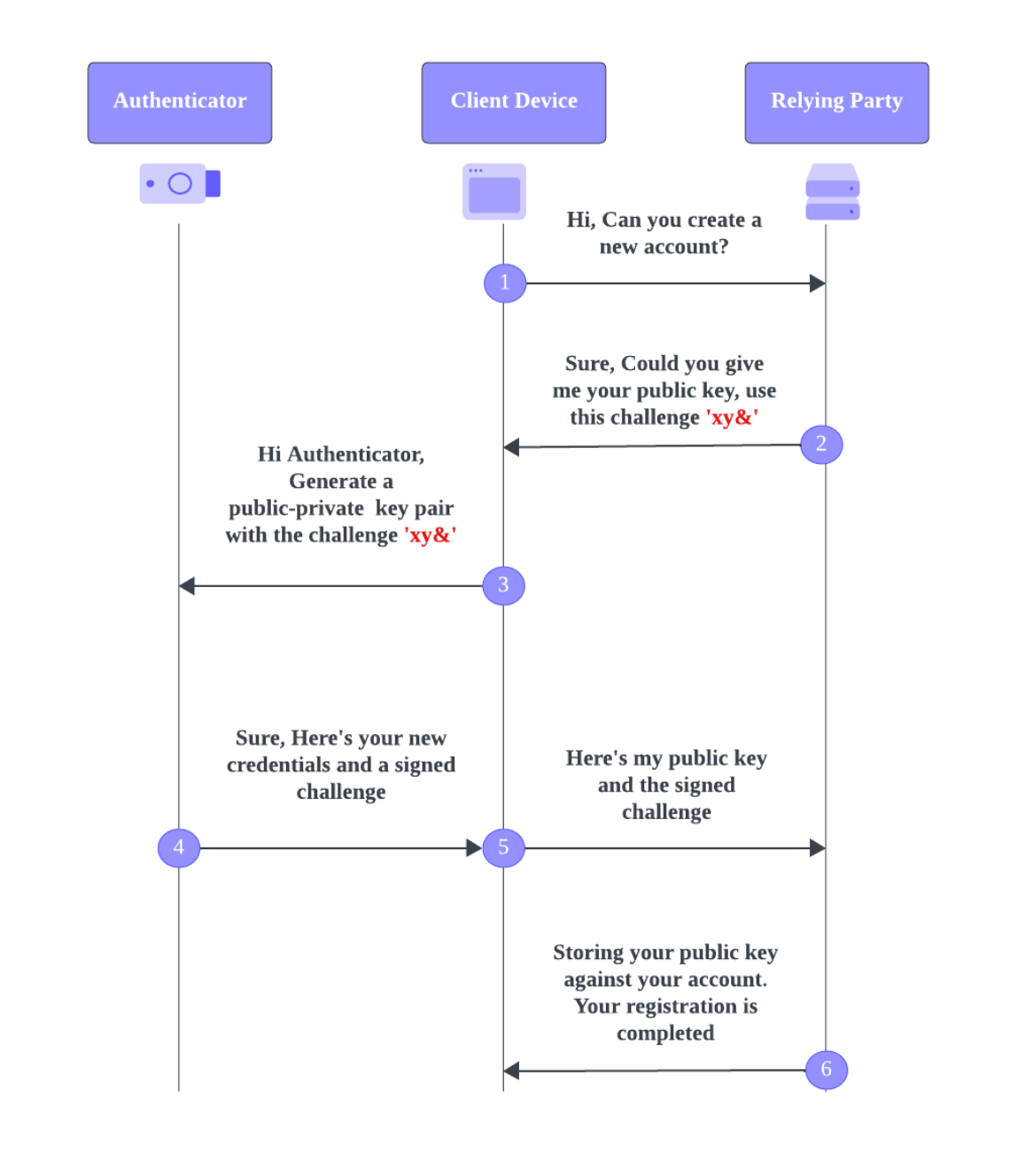
Registration Flow #
- A User visits a Relying Party(RP) website
- Initiating registration : RP generates a unique and cryptographically random challenge and communicates to the user’s browser that it wants to register a new public, private key pair.
- The user chooses an authenticator to generate a public, private key pair : The user selects their preferred authenticator(platform or roaming). The chosen authenticator generates a new public, private key pair and signs the challenge with those keys.
- The Authenticator sends back the user credentials : The private key is stored within the authenticator, while the public key is sent back to the website along with the signed challenge and optional private key ID.
- The RP stores the user credential : The website stores the user’s public key and the private key ID(if sent) and associates it with the user’s account for future authentication.
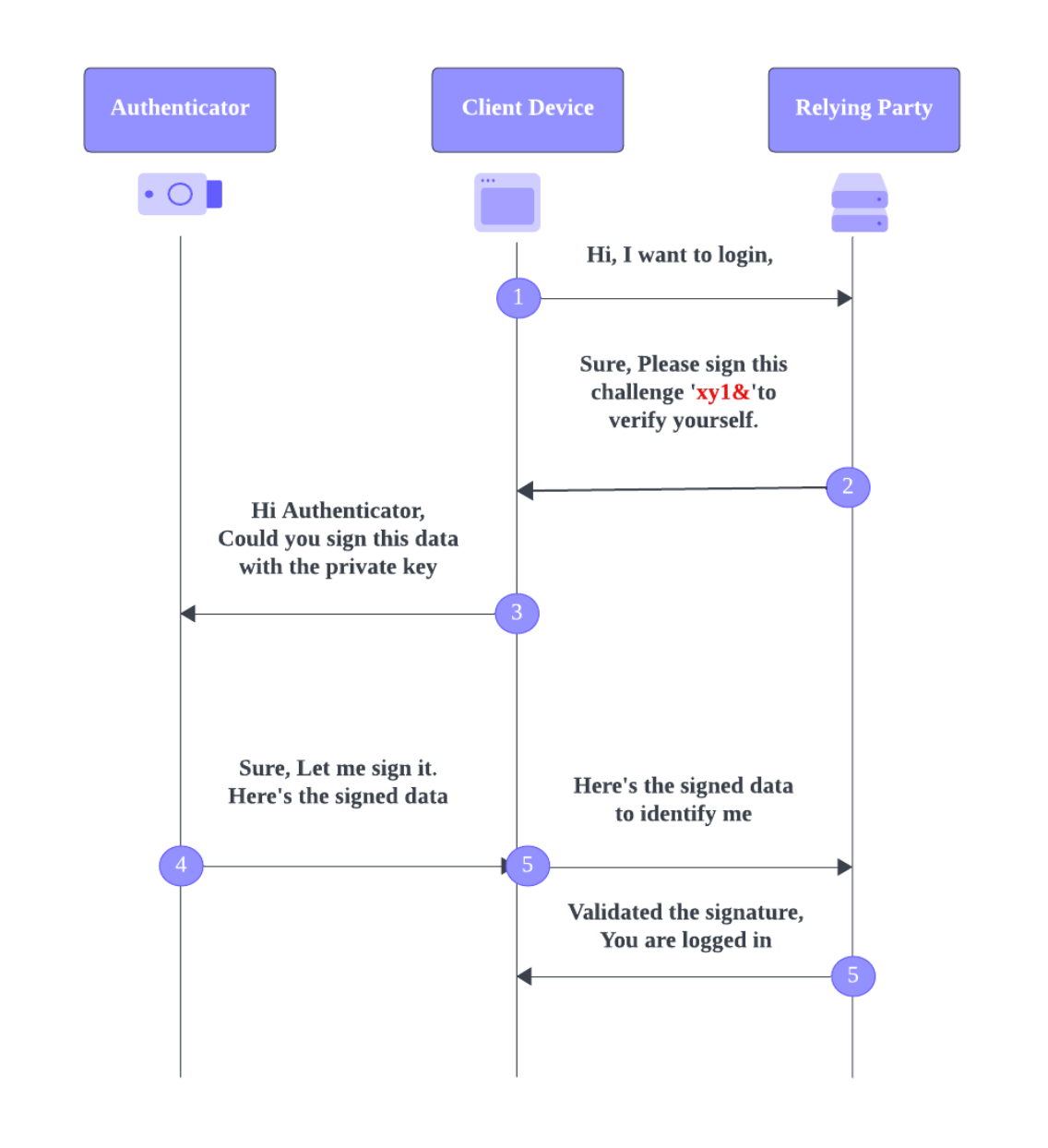
Authentication Flow #
- User visits the RP website :
- RP generates an authentication challenge : The RP generates a new challenge and sends it to the user’s browser.
- User requests authenticator to sign the challenge : The user selects the authenticator they used during registration, or the authenticator may be automatically detected and requested to sign the challenge.
- Authenticator signs the challenge : The authenticator signs the challenge with the private key stored during registration. The authenticator sends the signed response and the public key back to the website.
- User verification : The RP receives the signed response and the user’s public key. It verifies the response by checking the signature against the stored public key. If the verification is successful, the website grants the user access to the requested resources.